Written by: Patrick Carroll, Cultural Resource Management Advisor, Southwest NWT Field Unit, Parks Canada
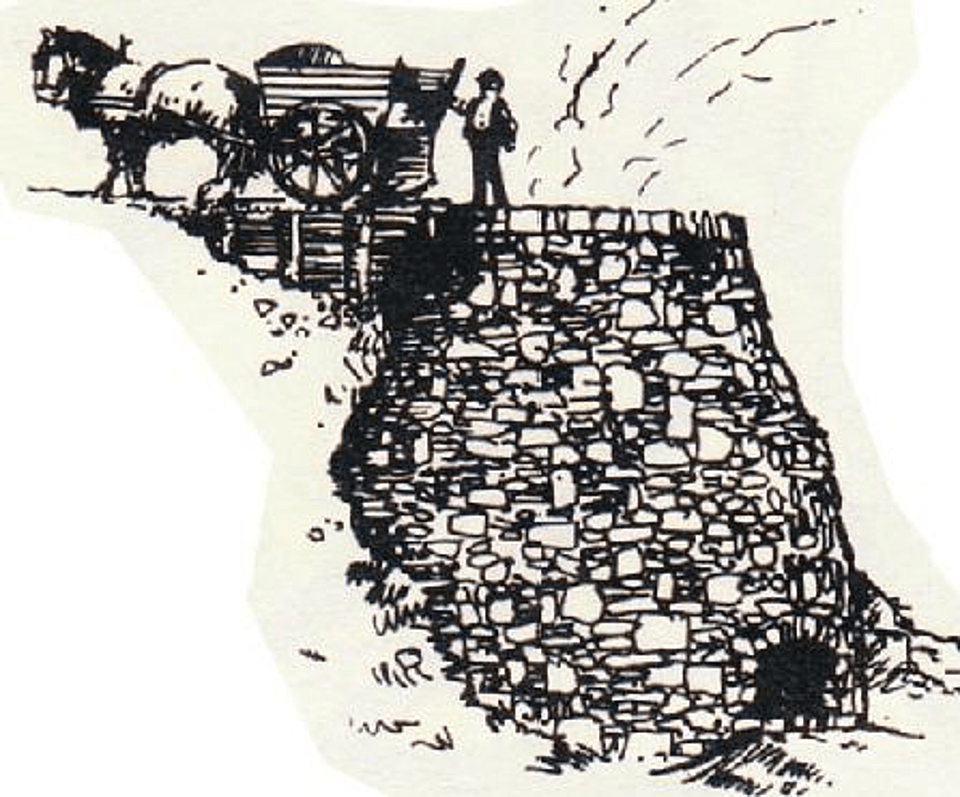
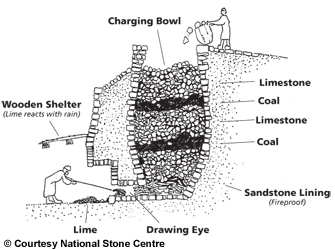
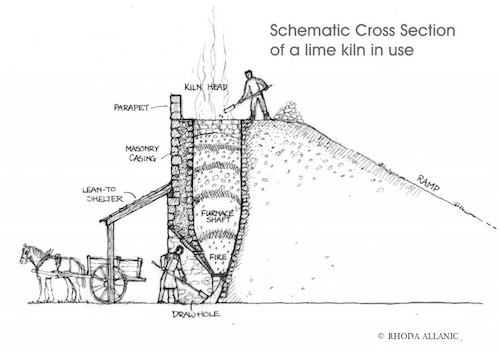
About 50 km upriver on the Slave River from Fitzgerald, Alberta, among a small cluster of islands named Stony Islands, you will find the remains of a stone lime kiln. Archaeologist Marc Stevenson documented the kiln (IjOu-5) and a nearby quarry (IjOu-6) during a survey of the Slave River in 1980. He described the kiln as a, “large semicircular limestone feature 4m in height.” The quarry is an exposed face of limestone just upriver from the kiln. All that we know about the history of the kiln is based on notes from a conversation Stevenson had with a Brother Seaurault. According to Stevenson, “The feature, according to an elderly informant, is the limestone furnace used by residents of Fort Chipewyan in the 1910’s and 1920’s to make whitewash for their log homes in the latter settlement.” It appears, therefore, to have been here for at least a century and is now showing the degradations of time, seasonal flooding and ice scouring.
The kiln is built into a natural alcove in the limestone exposure, set on a rocky shelf at a height to protect it from the impacts of seasonal high water and ice scouring on the Slave River. It consists of a semi-circular convex stone wall extending from the bedrock which, together, create the chimney. The height of the wall extends to the height of the top of the bedrock. A stoke hole on the bottom of the wall faces toward the river. An interesting feature of this kiln is that one side of the wall of the kiln does not abut directly against the limestone outcrop. The collapsing wall on the down-river side appears to have been built mostly flush to the bedrock face. The wall on the up-river side, though, remains in its original condition showing it was built with a 30-60 cm gap between the edge of the stone wall and the bedrock face. It is not known what purpose this gap might have provided for the operation of the kiln, although, it is easily wide enough to allow for a person to enter the cavity of the chimney.